376. Wiggle Subsequence
Description
A sequence of numbers is called a wiggle sequence if the differences between successive numbers strictly alternate between positive and negative. The first difference (if one exists) may be either positive or negative. A sequence with fewer than two elements is trivially a wiggle sequence.
For example,
[1,7,4,9,2,5]is a wiggle sequence because the differences (6,-3,5,-7,3) are alternately positive and negative. In contrast,[1,4,7,2,5]and[1,7,4,5,5]are not wiggle sequences, the first because its first two differences are positive and the second because its last difference is zero.Given a sequence of integers, return the length of the longest subsequence that is a wiggle sequence. A subsequence is obtained by deleting some number of elements (eventually, also zero) from the original sequence, leaving the remaining elements in their original order.
Example:
Input: [1,7,4,9,2,5]Output: 6The entire sequence is a wiggle sequence.
Input: [1,17,5,10,13,15,10,5,16,8]Output: 7There are several subsequences that achieve this length. One is [1,17,10,13,10,16,8].
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]Output: 2
Solution
题意:从给出序列中寻找最长的摆动序列并输出该子序列长度,摆动序列定义是按照一增一减的序列,其相邻的差分别一正一负。
1. 贪心法 Greedy
序列从最左开始,找连续递增序列的最大值为转折点,以及连续递减最小值为转折点,计数,最后得到的cnt值即为摆动序列并输出该子序列长度。分析图如下所示,不在拐点处的摆动序列的长度一定小于等于选择拐点处(峰值)的摆动序列。
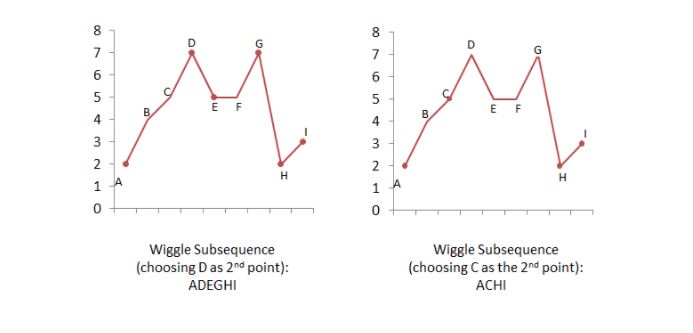 初始代码如下 (Java):
初始代码如下 (Java):
class Solution {
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length < 2)
{
return nums.length;
}
else
{
int temp = nums[0];
int cnt = 1;
int flag = 0;
if(nums[1] > nums[0]) {
flag = 1;
cnt ++;
temp = nums[1];
} else if (nums[1] < nums[0]) {
flag = -1;
cnt ++;
temp = nums[0];
}
for(int i=2; i<nums.length; i++)
{
if(nums[i] > nums[i-1]) {
if(flag == 1) {
if(nums[i] > temp) {
temp = nums[i];
}
}
else {
flag = 1;
cnt++;
temp = nums[i];
}
}
else if(nums[i] < nums[i-1]) {
if(flag == -1) {
if(nums[i] < temp) {
temp = nums[i];
}
} else {
flag = -1;
cnt++;
temp = nums[i];
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
}
}
优化后的代码如下(Java):
class Solution {
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length < 2)
{
return nums.length;
}
else
{
int prediff = nums[1] - nums[0];
int cnt = (prediff != 0) ? 2 : 1;
for(int i=2; i<nums.length; i++)
{
int diff = nums[i] - nums[i-1];
if((diff > 0 && prediff <= 0) || (diff < 0 && prediff >= 0))
{
cnt++;
prediff = diff;
}
}
return cnt;
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis: · Time complexity : O(n). We traverse the given array once. · Space complexity : O(1). No extra space is used.
2. 动态规划 Dynamic Programming
Linear Dynamic Programming(线性动态规划) 当前元素与前一个元素的关系有三种:大于、等于、小于。up[i]表示以第i个元素结尾的最后是上升的抖动序列的长度,down[i]表示以第i个元素结尾的最后是下降的抖动序列的长度。
- nums[i] > nums[i-1],表示序列在此处上升,所以之前的序列必须是下降的,则up[i] = down[i-1]+1,down[i] = down[i-1];
- nums[i] < nums[i-1],表示序列在此处下降,所以之前的序列必须是上升的,则down[i] = up[i-1]+1,up[i] = up[i-1];
- nums[i] == nums[i-1],表示序列在此处没有改变,则down[i] = down[i-1],up[i] = up[i-1];
- 最后找up[length-1]和down[length-1]最大的一个即可。
代码如下(Java):
public class Solution {
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length < 2)
return nums.length;
int[] up = new int[nums.length];
int[] down = new int[nums.length];
up[0] = down[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1]) {
up[i] = down[i - 1] + 1;
down[i] = down[i - 1];
} else if (nums[i] < nums[i - 1]) {
down[i] = up[i - 1] + 1;
up[i] = up[i - 1];
} else {
down[i] = down[i - 1];
up[i] = up[i - 1];
}
}
return Math.max(down[nums.length - 1], up[nums.length - 1]);
}
}
Complexity Analysis · Time complexity : O(n). Only one pass over the array length. · Space complexity : O(n). Two arrays of the same length are used for dp.
Space-Optimized Dynamic Programming(空间优化的动态规划)
public class Solution {
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length < 2)
return nums.length;
int down = 1, up = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] > nums[i - 1])
up = down + 1;
else if (nums[i] < nums[i - 1])
down = up + 1;
}
return Math.max(down, up);
}
}
Complexity Analysis · Time complexity : O(n). Only one pass over the array length. · Space complexity : O(1). Constant space is used.